由Linux中listen()函数谈开去
一、简介
1. 前言
本篇博文主要谈一谈Linux系统中,在使用socket套接字建立Tcp连接时,关于listen()函数的backlog参数的理解,同时,借由该问题,并结合具体的实践,尝试厘清Tcp连接的建立过程。
本篇博客编写主要参考借鉴了以下两篇博文,并在其基础上,加入了个人的一些思考与探索。
1. 深入探索 Linux listen() 函数 backlog 的含义
2. How TCP backlog works in Linux
下述内容的讨论,建立在对Tcp/Ip、socket有一定了解的基础上,相关的知识点,可以参考以下博文:
1.揭开Socket编程的面纱
2.Linux Socket编程(不限Linux)
2. 问题引入
当我们尝试在
Linux上通过Socket建立一个服务器,并接收客户端的连接请求时,服务器端程序通常需要执行以下流程:1. 使用创建 socket() 创建一个监听描述符
ListenFd2. 使用 bind() 为
ListenFd绑定一个本地的地址,以便于其它的socket(套接字),能够与其建立连接3. 使用 listen() 将
ListenFd设置为被动模式——表明自己乐意接受连接请求,并设置【连接建立队列的限制】。4. 调用 accept() 以接收具体的连接。
5. 数据交互。。。
服务器与客户端通过调用相关函数建立连接的流程如下所示:
图1:Tcp连接实现
注:在上图中,并未展示断开连接的过程
在平时的工程实践中,自己也都是照猫画虎, 知其然而不知其所以然。由于最近尝试写一个使用TCP构建的客户端/服务器公共框架的框架,在写作过程中,发现自己对于很多基础的操作都不明其意,基于此,才有了这边博文。
文章首先介绍socket的一些基本概念,接下来通过一个具体的实例,并结合相应的抓包分析,印证实际与理论是否相符。
二、原理介绍
1. Tcp三次握手
在学习计算机网络的相关知识时,想必大家对于Tcp三次握手的连接过程并不陌生:
图2: Tcp三次握手
正如上图所示:
- 客户端请求建立连接,然后进入SYN-SENT状态
- 处于LISTEN状态的服务器端在收到连接请求后,给客户端回复应答,同时进入SYN-RCVD状态
- 客户端在收到应答后,进入ESTABLISHED状态,同时再次发消息告知服务器端
- 服务器端在收到消息后,亦即进入ESTABLISHED状态
在完成上述交互过程后,Tcp 连接建立,两者即可进行后续的数据交互。
以上为建立连接的逻辑过程,看起来清晰易懂,似乎没有什么难以理解的地方,但是,倘若需要我们将三次握手过程与图一的实现联系起来呢?
根据自己以往的经验,具体的实现,与Tcp三次握手的原理图,应该是如下的对应关系:
图3: Tcp三次握手实现的错误理解
对于客户端而言:在调用connect()后进入SYN-SENT状态,同时阻塞,以等待服务器应答;在接收到应答后,则进入ESTABLISHED状态。
注:调用socket()到connect()之间的这段状态,我们暂且将其称为INIT状态
对于服务器而言:调用listen()后进入LISTEN状态,在调用accept()接收客户端的连接请求后,会短暂的进入SYN-RCVD状态,随后进入ESTABLISHED状态。
注:调用socket()到listen()之间的这段状态,我们暂且将其称为INIT状态
图中的状态划分,粗看的话,似乎也说的过去,完整体现了三次握手的过程,但事实是否真的如此呢?在展开具体的说明之前,首先需要对listen()函数进行介绍。
2. 关于backlog参数的理解
1 | int listen(int sockfd, int backlog); |
listen()将sockfd对应的描述符标记为被动模式,所谓被动模式的意思也就是说,可以用accept()来接受收到的连接请求。其中,backlog参数指定列了挂起连接队列可以增长的最大长度。
正如上文所说的,由于Tcp通过三次握手建立连接,一个连接在成功建立并进入ESTABLISHED状态前,会经历一段短暂的SYN-RCVD状态,之后就可以被accept()系统调用处理,并返回给应用。这意味着Tcp/Ip协议栈拥有两种方式来实现处于LISTEN状态的socket套接字的backlog队列:
- 方式1
The implementation uses a single queue, the size of which is determined by the backlog argument of the listen syscall. When a SYN packet is received, it sends back a SYN/ACK packet and adds the connection to the queue. When the corresponding ACK is received, the connection changes its state to ESTABLISHED and becomes eligible for handover to the application. This means that the queue can contain connections in two different state: SYN RECEIVED and ESTABLISHED. Only connections in the latter state can be returned to the application by the accept syscall.
——《How TCP backlog works in Linux》
实现使用单个队列,其尺寸由listen()的backlog参数决定。处于被动模式的socket在收到一个SYN报文后,它返回一个SYN/ACK报文,并将该链接加入队列。在收到相应的ACK应答报文后,此连接将状态改为ESTABLISHED,此后,才有资格被移交给应用程序(注:才可以用于后续的交互)。以上也就意味着,该队列可能同时包含处于SYN-RCVD以及ESTABLISHED两种状态的连接。只有处于后一种状态的连接,方可以被accept()处理,并返回给用户。
- 方式2
The implementation uses two queues, a SYN queue (or incomplete connection queue) and an accept queue (or complete connection queue). Connections in state SYN RECEIVED are added to the SYN queue and later moved to the accept queue when their state changes to ESTABLISHED, i.e. when the ACK packet in the 3-way handshake is received. As the name implies, the accept call is then implemented simply to consume connections from the accept queue. In this case, the backlog argument of the listen syscall determines the size of the accept queue.
——《How TCP backlog works in Linux》
此种实现使用两个队列:SYN队列(连接未完成队列),以及accept队列(已完成连接的队列)。SYN-RCVD状态的连接被加入SYN队列,当连接状态变为ESTABLISHED后,则被移入到accept队列(例如,在接收到三次握手中的ACK报文时)。顾名思义,accept()调用,其实现就是为了接受来自accept队列的连接(注:所谓接受连接,意即该连接已经建立,可以通过调用accept()被返回给用户,并用于后续交互。随后,该连接也就被从accept队列中移除)。对于此种方式,listen()调用的backlog参数,决定了accept队列的大小。
Historically, BSD derived TCP implementations use the first approach. That choice implies that when the maximum backlog is reached, the system will no longer send back SYN/ACK packets in response to SYN packets. Usually the TCP implementation will simply drop the SYN packet (instead of responding with a RST packet) so that the client will retry.
The BSD implementation does use two separate queues, but they behave as a single queue with a fixed maximum size determined by (but not necessary exactly equal to) the backlog argument:The queue limit applies to the sum of […] the number of entries on the incomplete connection queue […] and […] the number of entries on the completed connection queue […].
从历史上看,派生自BSD的Tcp实现使用第一种方案。该选择意味着,当队列达到backlog所定义的最大值时,系统不会发送SYN/ACK报文去回应SYN报文。通常,Tcp实现只会丢弃SYN报文(而不是应答RST报文),以便客户端可以重试。
BSD实现确实是用两个队列,然而它们的行为就如同是由backlog参数决定大小的单个队列。
队列限制适用于未完成连接队列的条目数与已完成连接条目数的总和。
On Linux, things are different, as mentioned in the man page of the listen syscall:
The behavior of the backlog argument on TCP sockets changed with Linux 2.2. Now it specifies the queue length for completely established sockets waiting to be accepted, instead of the number of incomplete connection requests. The maximum length of the queue for incomplete sockets can be set using /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog.
在Linux上,情况则有所不同,以下是man page中关于listen系统调用的内容:
Tcp socket的backlog参数的行为在Linux2.2中有所改变。它现在指定了等待被接受的连接已完成的套接字的队列(注:即accept队列)的长度,而不是未完成的连接请求的个数(注:即SYN队列中所包含的连接个数)。 未完成连接队列的最大长度可以被设定为/proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog。
为了验证实际是否与上述理论是一致的,我们将在下文中通过具体的例程,并结合具体的抓包数据,对Tcp的连接过程进行分析。
三、实验与分析
1. 实验环境
处理器名称:Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-4170 CPU @ 3.70GHz
系统版本:CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
编译器版本:gcc version 4.4.7 20120313
2. 例程介绍
实验使用的例程包括Client与Server两部分,具体地址详见。
- 客户端代码片段
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
struct sockaddr_in stServAddr;
using namespace std;
/**
*@brief 格式化错误信息
*
*
*@param int errnoflag
*@param int error
*@param const char *fmt
*@param va_list ap
*
*@return
*
*
*@author Litost_Cheng
*@date 2019年1月21日
*@note 新生成函数
*/
static void ErrDoit(int errnoflag, int error, const char *fmt, va_list ap)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
vsnprintf(buf, MAXLINE-1, fmt, ap);
if (errnoflag)
snprintf(buf + strlen(buf), MAXLINE - strlen(buf) - 1, ": errno[%d] %s",
error, strerror(error));
strcat(buf, "\n");
fflush(stdout); /* in case stdout and stderr are the same */
fputs(buf, stderr);
fflush(NULL); /* flushes all stdio output streams */
}
/**
*@brief 判断条件,打印errno并退出
*
*
*@param bool bCondition
*@param const char *fmt
*@param ...
*
*@return
*
*
*@author Litost_Cheng
*@date 2019年5月11日
*@note 新生成函数
*
*/
bool CondJudgeExit(bool bCondition, const char *fmt, ...)
{
if (!bCondition)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
ErrDoit(1, errno, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
return bCondition;
}
void *func(void *)
{
int nConnFd;
nConnFd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
printf("nConnFd : %d\n",nConnFd);
///在没个子线程中,都会尝试与服务器连接连接,并返回结果
if ((connect(nConnFd,(struct sockaddr *)&stServAddr,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)) == -1))
{
printf("[nConnFd] Connect failed: [%s]\n", strerror(errno));
return (void *)-1;
}
else
{
printf("Connect succeed!\n");
stringstream strStream;
strStream << "[" << nConnFd << "]" << "Send Message";
printf("strStream is [%s]\n", strStream.str().c_str());
if (-1 == write(nConnFd, strStream.str().c_str(), strStream.str().size()))
{
printf("[nConnFd] Connect failed: [%s]\n", strerror(errno));
return (void *)-1;
}
else
{
printf("[nConnFd] Send succeed!\n", nConnFd);
}
}
while(1) {}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
memset(&stServAddr,0,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
stServAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
stServAddr.sin_port = htons(PORT);
inet_aton("127.0.0.1",(struct in_addr *)&stServAddr.sin_addr);
//创建线程并且等待线程完成
pthread_t nPid[THREAD_NUM];
//system("netstat -atn | grep '17777'");
//printf("netstat -atn\n");
for(int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUM; ++i)
{
pthread_create(&nPid[i],NULL,&func,NULL);
}
sleep(3);
//system("netstat -atn | grep '17777'");
//printf("netstat -atn\n");
for(int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUM; ++i)
{
pthread_join(nPid[i], NULL);
}
return 0;
}
以上,为了搞清backlog参数的真实含义,客户端进程会创建THREAD_NUM个线程,来向服务器端发起连接请求,并返回相应的结果。
- 服务器端代码片段
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
using namespace std;
/**
*@brief 格式化错误信息
*
*
*@param int errnoflag
*@param int error
*@param const char *fmt
*@param va_list ap
*
*@return
*
*
*@author Litost_Cheng
*@date 2019年1月21日
*@note 新生成函数
*/
static void ErrDoit(int errnoflag, int error, const char *fmt, va_list ap)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
vsnprintf(buf, MAXLINE-1, fmt, ap);
if (errnoflag)
snprintf(buf + strlen(buf), MAXLINE - strlen(buf) - 1, ": errno[%d] %s",
error, strerror(error));
strcat(buf, "\n");
fflush(stdout); /* in case stdout and stderr are the same */
fputs(buf, stderr);
fflush(NULL); /* flushes all stdio output streams */
}
/**
*@brief 判断条件,打印errno并退出
*
*
*@param bool bCondition
*@param const char *fmt
*@param ...
*
*@return
*
*
*@author Litost_Cheng
*@date 2019年5月11日
*@note 新生成函数
*
*/
bool CondJudgeExit(bool bCondition, const char *fmt, ...)
{
if (!bCondition)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
ErrDoit(1, errno, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
return bCondition;
}
/**
*@brief 展示连接信息
*
*
*@param bool bCondition
*@param const char *fmt
*@param ...
*
*@return void
*
*
*@author Litost_Cheng
*@date 2019年5月11日
*@note 新生成函数
*
*/
void Display()
{
system("netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2");
printf("netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2\n");
//system("lsof -nP -iTCP | grep '17777'");
//printf("lsof -nP -iTCP | grep '17777'\n");
}
char *pCmd[5];
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int nConLen;
int nSockFd,nConnFd;
struct sockaddr_in stServAddr,stConnAddr;
int nCmd = 0;
pCmd[0] = "socket";
pCmd[1] = "bind";
pCmd[2] = "listen";
pCmd[3] = "accept_once";
pCmd[4] = "accept_times";
printf("Please input the Cmd: \n");
for(int n=0; n<5; n++)
{
printf("\t[%d]: [%s]\n", n, pCmd[n]);
}
std::cin >> nCmd;
std::string strSysCmd = "tcpdump -i lo -s 0 -w ./Tcpdump_";
strSysCmd += pCmd[nCmd];
strSysCmd += ".cap";
strSysCmd += " &";
system(strSysCmd.c_str());
printf("[%s]\n", strSysCmd.c_str());
do
{
printf("Start:");
Display();
//创建套接字
CondJudgeExit(((nSockFd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0)) != -1), "Create socket failed!\n");
if (0 == nCmd)
{
break;
}
//为套接字绑定地址,需要注意字节序
memset(&stServAddr,0,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
stServAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
stServAddr.sin_port = htons(PORT);
stServAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
CondJudgeExit((bind(nSockFd,(struct sockaddr *)&stServAddr,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)) != -1), "bind failed!\n");
if (1 == nCmd)
{
break;
}
//设置为被动模式
CondJudgeExit((listen(nSockFd,BACKLOG) != -1), "listen filed!\n");
if (2 == nCmd)
{
break;
}
//accept once
nConLen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
//sleep(10); //sleep 10s之后接受一个连接
//该套接字默认为阻塞模式,所以,倘若没有接受的一个成功建立的连接,则会一直阻塞在这里
accept(nSockFd,(struct sockaddr *)&stConnAddr,(socklen_t *)&nConLen);
printf("I have accept one Connect: [%s], port[%d] \n", inet_ntoa(stConnAddr.sin_addr), ntohs(stConnAddr.sin_port));
if (3 == nCmd)
{
break;
}
printf("Pending on [%s]\n", pCmd[nCmd]);
while(1)
{
sleep(3); //周期性接受连接请求
printf("I will accept one\n");
accept(nSockFd,(struct sockaddr *)&stConnAddr,(socklen_t *)&nConLen);
printf("I have accept one Connect: [%s], port[%d] \n", inet_ntoa(stConnAddr.sin_addr), ntohs(stConnAddr.sin_port));
Display();
}
}
while(0);
while(1)
{
printf("Pending on [%s]\n", pCmd[nCmd]);
Display();
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
对于服务器端进程而言,我们手动将backlog设置为BACKLOG,以判断其如何处理过量的连接;此外,为了厘清Tcp三次握手与具体实现之间的联系,该例程会根据用户输入的不同的选项,将程序阻塞在不同阶段,并结合对应时刻的连接状态以及抓包数据,确定当前连接所处的状态。
在开始具体的实验前,有以下几点是需要我们注意的:
- 为了理解
backlog参数的实际含义,实验过程中,我们要求Client程序中的THREAD_NUM参数应该要大于Server中的BACKLOG,以认为造成过量的连接请求。 - 代码的编译使用自动的
makefile文件模板MakeFileTemplate,用户只需执行make命令,即可生成相应的可执行文件。 - 连接状态的获取使用netstat获取
- 抓包数据的获取使用Tcpdump,并配合Wireshark工具对抓包进行分析,关于两工具的使用,详见该链接:聊聊 tcpdump 与 Wireshark 抓包分析。
3. 分步实验
在具体的实验过程中,我们会将Server分别阻塞以下几个阶段,同时会附上相应的程序输出(Client,Server),连接状态,以及抓包数据,以方便读者能够有一个直观的认识。
1. Server阻塞于socket()创建后
实验数据
客户端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14[root@litost Client]# ./Client
nConnFd : 3
nConnFd : 4
nConnFd : 5
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
nConnFd : 6
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
nConnFd : 7
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
nConnFd : 8
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
[root@litost Client]#服务器输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15[root@litost Server]# ./Server
Please input the Cmd:
[0]: [socket]
[1]: [bind]
[2]: [listen]
[3]: [accept_once]
[4]: [accept_times]
0
[tcpdump -i lo -s 0 -w ./Tcpdump_socket.cap &]
Start:netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [socket]
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
tcpdump: listening on lo, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes
Pending on [socket]
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2抓包数据
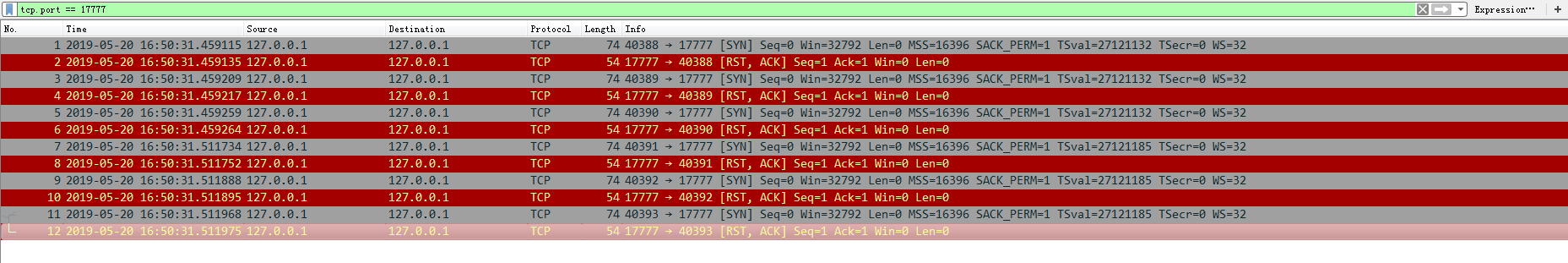
- 数据分析
从以上实验数据,我们不难看出,当Client尝试去连接阻塞在socket()状态的Server时,连接全部失败,从抓包获取到的数据来看,针对客户端的SYN请求,Server直接回复了RST,而从Client调用accept()返回的错误结果来看,显示连接被拒绝。
因此在该阶段,Client应该是进入了短暂的SYN-SENT阶段(注:并未从netstat抓取到有关数据,可能是由于连接迅速被断开导致),随后连接即被拒绝,而Server则是处于CLOSED状态。
2. Server阻塞于bind()后
实验数据
客户端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14[root@litost Client]# ./Client
nConnFd : 3
nConnFd : 4
nConnFd : 5
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
nConnFd : 6
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
nConnFd : 7
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
nConnFd : 8
[nConnFd] Connect failed: [Connection refused]
[root@litost Client]#服务器端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15[root@litost Server]# ./Server
Please input the Cmd:
[0]: [socket]
[1]: [bind]
[2]: [listen]
[3]: [accept_once]
[4]: [accept_times]
1
[tcpdump -i lo -s 0 -w ./Tcpdump_bind.cap &]
Start:netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [bind]
tcpdump: listening on lo, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [bind]
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2抓包数据
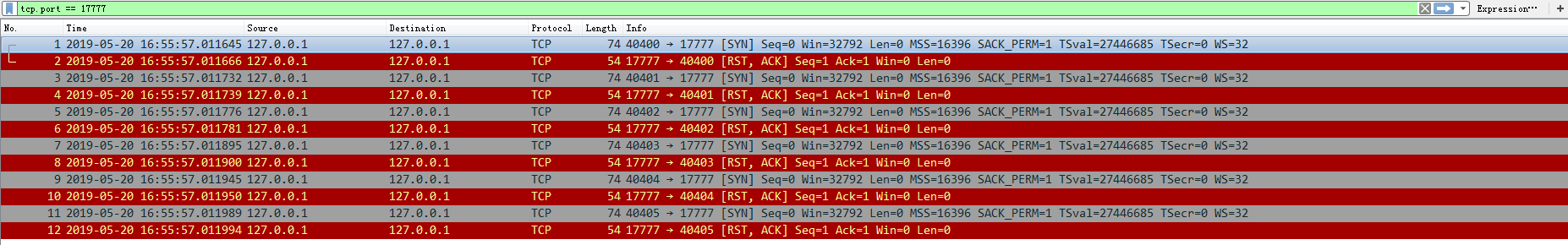
- 数据分析
在实际的实验过程中,对于Client而言,其情况与阻塞在socket()时保持一致:连接全部失败。
因此在该阶段,Client应该也是进入了短暂的SYN-SENT阶段(注:并未从netstat抓取到有关数据,可能是由于连接迅速被断开导致),随后连接即被拒绝,而Server一直处于CLOSED状态。
3. Server阻塞于listen()后
实验数据
客户端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27[root@litost Client]# ./Client
nConnFd : 3
nConnFd : 4
nConnFd : 5
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[5]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[4]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[3]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 6
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[6]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 7
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[7]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 8
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[8]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
^C
[root@litost Client]#服务器端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59[root@litost Server]# ./Server
Please input the Cmd:
[0]: [socket]
[1]: [bind]
[2]: [listen]
[3]: [accept_once]
[4]: [accept_times]
2
[tcpdump -i lo -s 0 -w ./Tcpdump_listen.cap &]
Start:netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [listen]
tcpdump: listening on lo, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [listen]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [listen]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40355 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40356 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40352 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40353 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40354 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40352 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40353 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40354 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40355 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40356 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 1 127.0.0.1:40357 127.0.0.1:17777 SYN_SENT
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [listen]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40355 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40356 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40352 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40353 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40354 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40352 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40353 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40354 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40355 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40356 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 1 127.0.0.1:40357 127.0.0.1:17777 SYN_SENT
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [listen]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40355 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40356 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40357 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40352 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40353 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40354 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40352 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40353 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40354 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40355 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40356 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40357 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED抓包数据
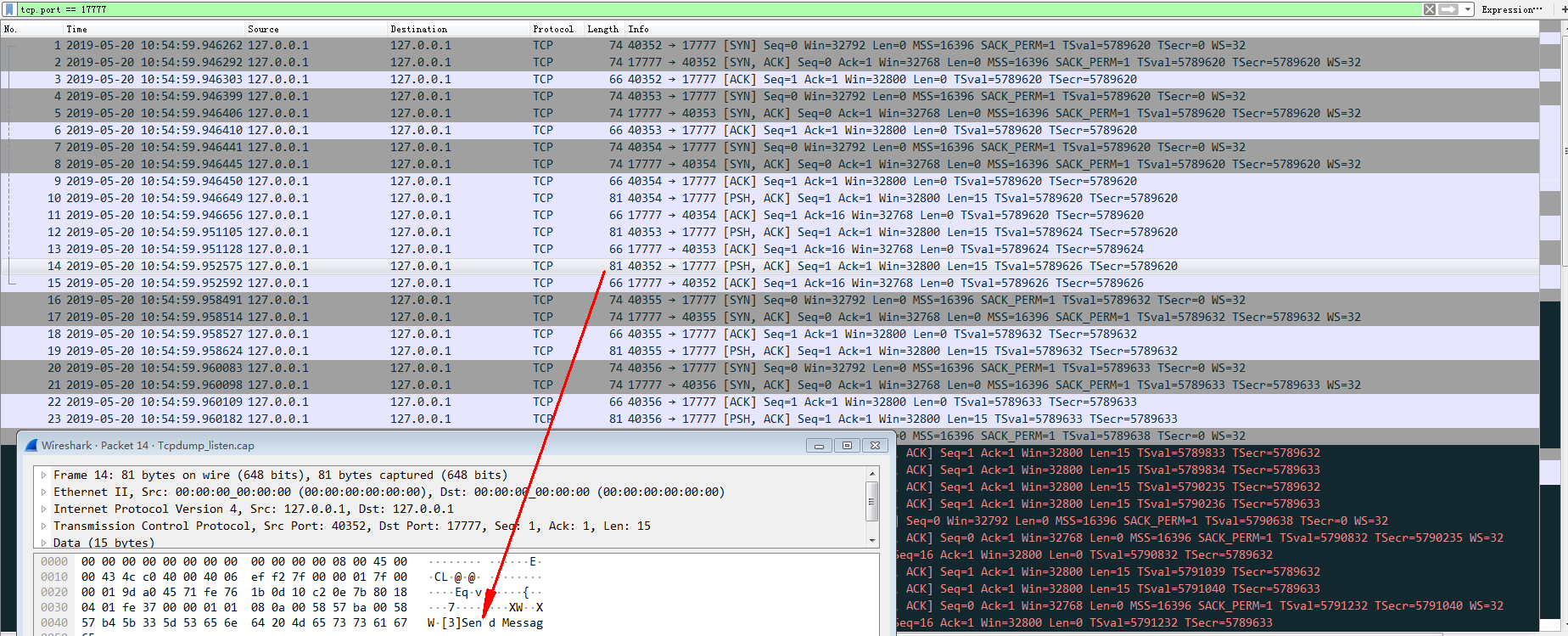
- 数据分析
在实际的实验过程中,对于Client而言,从connect()以及write()的结果来看,所有的连接都已成功建立,且处于ESTABLISHED状态。
但是,对于Server而言,有三个套接字(端口分别为:40352,40353,40354)处于ESTABLISHED状态,剩余的三个则仍处于SYN_RECV(但是需要注意的是,我们是将backlog的值设置为2)。同时,我们结合具体的抓包数据进行分析:针对所有连接而言,Tcp三次握手过程,都已完成。由此说明,对于处于被动模式的套接字(调用listen()后),能够自动处理接收到的连接请求,并完成三次握手的交互。同时,会将backlog + 1数量的连接放置于accept队列。
因此在该阶段,Client都处于ESTABLISHED阶段,Server则有backlog + 1数量的连接处于ESTABLISHED,剩余则是处于SYN_RECV状态。
4. Server阻塞于accept()一次后
实验数据
客户端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27[root@litost Client]# ./Client
nConnFd : 3
nConnFd : 4
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[4]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[3]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 5
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[5]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 6
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[6]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 7
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[7]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 8
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[8]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
^C
[root@litost Client]#服务器端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41[root@litost Server]# ./Server
Please input the Cmd:
[0]: [socket]
[1]: [bind]
[2]: [listen]
[3]: [accept_once]
[4]: [accept_times]
3
[tcpdump -i lo -s 0 -w ./Tcpdump_accept_once.cap &]
Start:netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
tcpdump: listening on lo, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes
I have accept one Connect: [127.0.0.1], port[42653]
Pending on [accept_once]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40362 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40363 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40358 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40359 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40360 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40361 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40358 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40359 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40360 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40361 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40362 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40363 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
Pending on [accept_once]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40362 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40363 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40358 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40359 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40360 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40361 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40358 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40359 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40360 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40361 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40362 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40363 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED抓包数据
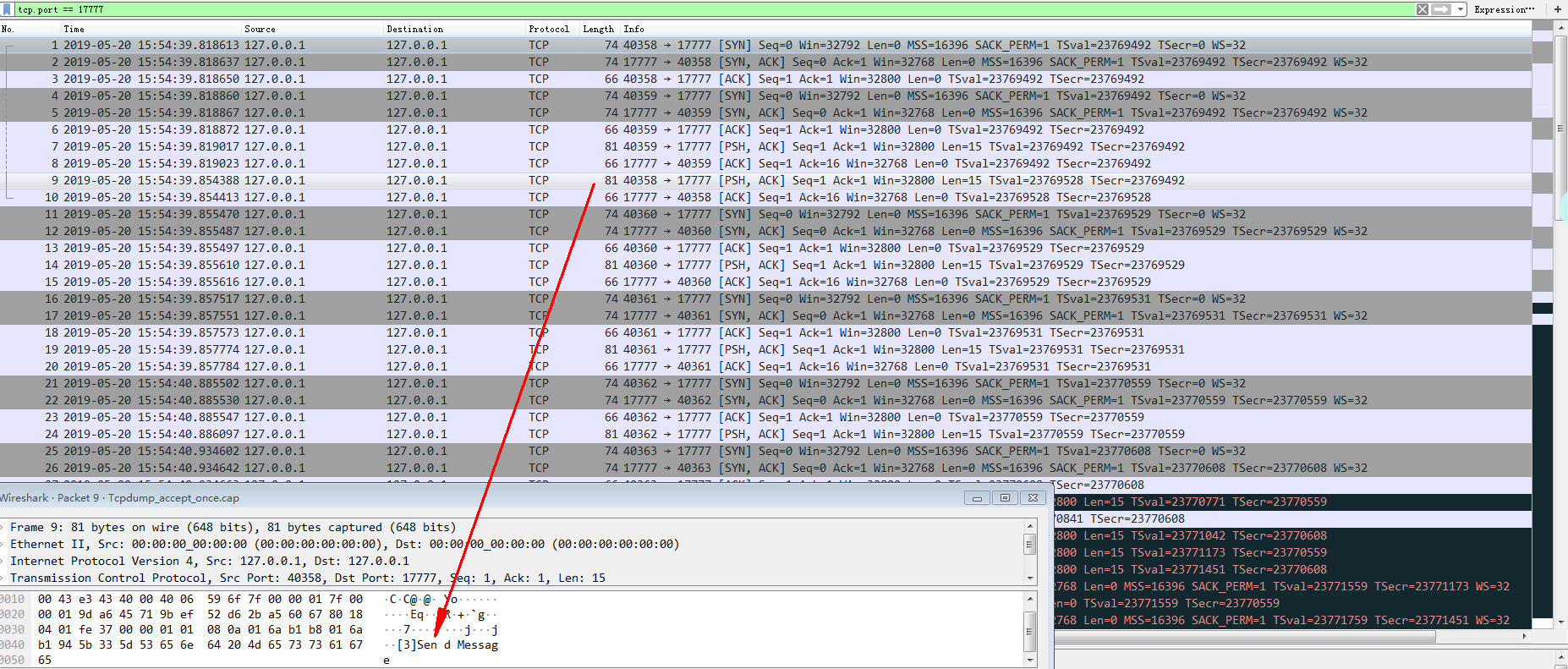
- 数据分析
在实际的实验过程中,对于Client而言,其状态与阻塞在listen()时,保持一致,为ESTABLISHED状态。
但是,对于Server而言,相比于阻塞在listen()时,有四个套接字(端口分别为:40358,40359,40360,40361)处于ESTABLISHED状态,剩余两个则仍处于SYN_RECV。结合相应的抓包数据,所有的连接都完成了Tcp三次握手的连接过程,由于我们调用了一次accept(),因此,相较于阻塞在listen()时(有3个套接字成功建立),对于Server端而言,一共有4个套接字处于ESTABLISHED状态,而这也与前文所述的方式2一致。
因此在该阶段,Client都处于ESTABLISHED阶段,Server则有backlog + 1 + 1(成功调用了一次accept())数量的连接处于ESTABLISHED,剩余则是处于SYN_RECV状态。
5. Server阻塞于accept()多次
实验数据
客户端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27[root@litost Client]# ./Client
nConnFd : 3
nConnFd : 4
nConnFd : 5
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[4]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[5]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[3]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 6
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[6]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 7
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[7]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
nConnFd : 8
Connect succeed!
strStream is [[8]Send Message]
[nConnFd] Send succeed!
^C
[root@litost Client]#服务器端输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60[root@litost Server]# ./Server
Please input the Cmd:
[0]: [socket]
[1]: [bind]
[2]: [listen]
[3]: [accept_once]
[4]: [accept_times]
4
[tcpdump -i lo -s 0 -w ./Tcpdump_accept_times.cap &]
Start:netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
tcpdump: listening on lo, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes
I have accept one Connect: [127.0.0.1], port[40382]
Pending on [accept_times]
I will accept one
I have accept one Connect: [127.0.0.1], port[40383]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40386 SYN_RECV
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40387 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40382 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40383 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40384 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40385 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40382 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40383 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40384 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40385 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40386 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40387 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
I will accept one
I have accept one Connect: [127.0.0.1], port[40384]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40387 SYN_RECV
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40382 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40383 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40384 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40385 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40386 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40382 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40383 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40384 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40385 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40386 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 15 127.0.0.1:40387 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
netstat -atn | grep '17777' | sort -n -t : -k 2
I will accept one
I have accept one Connect: [127.0.0.1], port[40385]
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:17777 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40382 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40383 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40384 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40385 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40386 ESTABLISHED
tcp 15 0 127.0.0.1:17777 127.0.0.1:40387 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40382 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40383 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40384 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40385 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40386 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:40387 127.0.0.1:17777 ESTABLISHED抓包数据
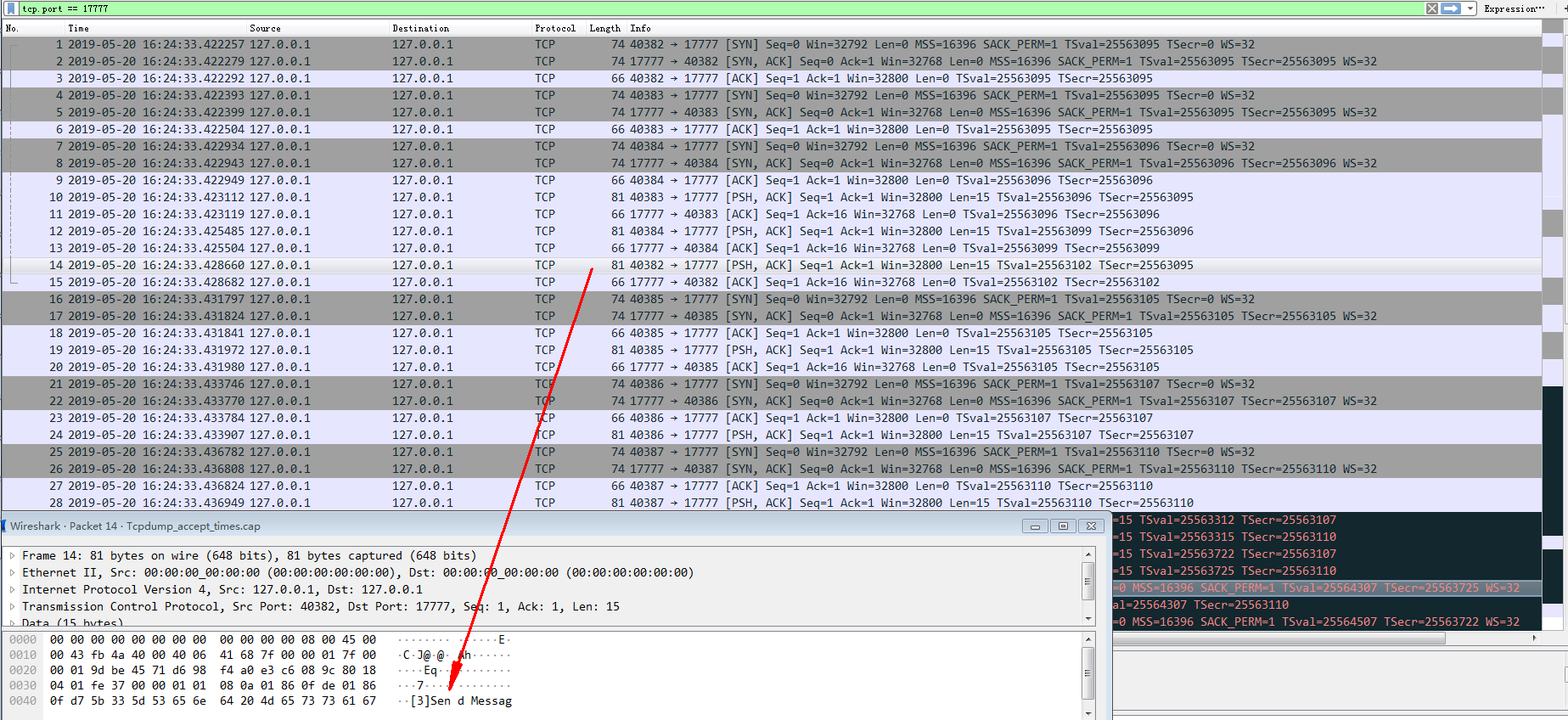
- 数据分析
在实际的实验过程中,对于Client而言,其状态与阻塞在listen()时,保持一致,为ESTABLISHED状态。
对于Server而言,结果正如欲想的一致,在调用3次accept()后,所有的连接都进入了ESTABLISHED。
因此在该阶段,Client都处于ESTABLISHED阶段,Server则有backlog + 1 + 3(成功调用了三次accept()后)数量的连接处于ESTABLISHED。
4. 实验结果分析
通过对以上分布实验的结果的分析,我认为在之前对于linux中Tcp三次握手实现的理解是错误的。正确的理解应该是如下图所示:
图4: 关于Tcp三次握手实现的正确的理解
主要存在以下几点误区:
- 在
Server成功调用listen()后,相应的套接字——我们暂且将其称为A(注:该套接字唯一作用就是用来接受连接请求),将进入被动模式,之后A其实就一直处于监听状态LISTEN。 Client调用connect()发起连接请求,处于监听状态的套接字A在收到连接请求后,首先会将其存储在前文提到的SYN队列,并将相应的套接字——我们将其称为B,设置为SYN-RCVD,并发送应答给Client。在收到Client后,B进入ESTABLISHED状态。但需要注意的是,此时的B应该仍位于SYN队列,只有在判断accept队列未满(小于backlog+ 1)时,才会将其转移到accept队列。
由于并未看过系统源码,以上仅是结合相应实验的到的结论,仅为个人理解,如有谬误,还望各位批评指正。此外,针对不同的系统,结果可能仍有不同。
三、参考与链接
深入探索 Linux listen() 函数 backlog 的含义:https://blog.csdn.net/yangbodong22011/article/details/60399728
How TCP backlog works in Linux:http://veithen.io/2014/01/01/how-tcp-backlog-works-in-linux.html
使用TCP构建的客户端/服务器公共框架:https://github.com/0Litost0/TcpClientServerFramework
MakeFileTemplate:https://github.com/0Litost0/MakeFileTemplate
netstat指令:https://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2013/03/08/2949194.html
聊聊 tcpdump 与 Wireshark 抓包分析:https://www.jianshu.com/p/8d9accf1d2f1
五、文档信息
作者: Litost_Cheng
发表日期:2019年05月20日
更多内容:
